3D printing has revolutionized manufacturing, prototyping, and DIY projects. However, before you can print anything, you need a reliable CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software to create or modify 3D models.
For beginners, choosing the right CAD software can be overwhelming. Some programs are too complex, while others lack essential features. To help you out, we’ve compiled a list of the best 3D printing CAD software for beginners in the USA, considering ease of use, functionality, and affordability.
Table of Contents
- What is CAD Software for 3D Printing?
- Key Features to Look for in 3D Printing CAD Software
- Best 3D Printing CAD Software for Beginners
- How to Choose the Right CAD Software for Your Needs
- Free vs. Paid CAD Software: Which is Better?
- Common Mistakes Beginners Make with 3D Printing CAD
- FAQs About 3D Printing CAD Software
1. What is CAD Software for 3D Printing?
CAD software allows users to design, modify, and optimize 3D models before sending them to a 3D printer. These tools range from simple drag-and-drop interfaces (great for beginners) to advanced parametric modeling (used by engineers).
Most CAD software exports files in STL or OBJ formats, which are compatible with 3D printers. Some programs also include slicing features, converting models into printable layers.
2. Key Features to Look for in 3D Printing CAD Software
When choosing CAD software for 3D printing, consider:
✅ User-Friendliness – Easy to learn for beginners.
✅ 3D Modeling Capabilities – Supports solid, mesh, and parametric modeling.
✅ Export Formats – STL, OBJ, and STEP compatibility.
✅ Community & Support – Active forums and tutorials.
✅ Price – Free vs. paid options.
✅ System Requirements – Works on your PC/Mac.
3. Best 3D Printing CAD Software for Beginners
1. TinkerCAD
Best for: Absolute beginners, kids, and educators.
Tinkercad is probably the most beginner-friendly 3D printing software out there, and I wanted to see if it was just for kids and hobbyists or if it could handle more serious printing needs. Unlike the other tools I evaluated, which focus on parametric modeling, industrial workflows, or advanced simulation, Tinkercad is all about accessibility.
It’s a web-based program that lets you drag, drop, and combine shapes to create 3D models, making it perfect for someone who has never worked with CAD before.
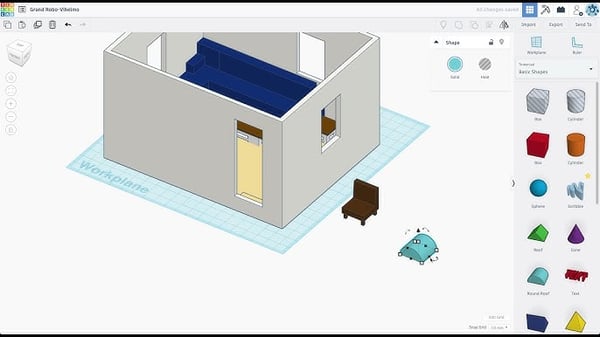
One thing yanatec reviewers often mention about Tinkercad is how fast it is to get started. There’s no software to install and no steep setup, just open a browser, create an account, and you’re designing within minutes. For users intimidated by traditional CAD tools, Tinkercad’s simplicity is a breath of fresh air.
The built-in shape library is another highlight. It includes geometric solids, text, and even basic mechanical parts like gears, which makes creating simple objects, keychains, nameplates, enclosures, quick and intuitive. Unlike tools that rely on constraints or precise parametric inputs, Tinkercad is entirely visual: you drag, resize, and combine objects freely. It’s no surprise that it’s a favorite in classrooms and maker spaces.
The block-based coding feature also stands out. It introduces beginners to procedural modeling by letting them generate shapes with simple scripts. While it doesn’t offer the depth of parametric modeling seen in platforms like SOLIDWORKS or Fusion 360, reviewers say it’s a great starting point for teaching code-based design.
That said, Tinkercad does have its limitations, especially for more advanced 3D printing workflows. Precision tools are lacking, so you can’t define exact alignments, tolerances, or fit constraints. If you’re designing functional parts that need to snap together or meet strict mechanical requirements, this platform can feel too basic.
File handling is another drawback. Because it runs entirely in a browser, yanatec users report that Tinkercad struggles with large or high-polygon models. Trying to import detailed STLs or scanned meshes often leads to lag or unresponsiveness, making it less ideal for complex edits or advanced projects.
Key Features:
✔ No installation required (cloud-based)
✔ Pre-built shapes and templates
✔ Direct export to STL for 3D printing
✔ Interactive tutorials for quick learning
Pros:
✅ 100% free
✅ Extremely easy to use
✅ Great for educational purposes
Cons:
❌ Limited advanced features
❌ Not suitable for complex engineering designs
Pricing: Free
2. Fusion 360
Best for: Hobbyists, engineers, and professionals.
Autodesk Fusion is one of the most widely used CAD tools in engineering, product design, and manufacturing, but I wanted to see how well it works specifically for 3D printing. Since it’s a hybrid of parametric, direct, and sculpting modeling, it offers more flexibility than software that only focuses on structured, mechanical design. Unlike simpler programs, it also has simulation, stress testing, and assembly tools, making it useful for designing functional parts rather than just decorative prints.
One feature that gets attention in reviews is Autodesk Fusion’s built-in slicer—something not commonly found in CAD platforms. Integrated within the Manufacturing workspace, it allows users to generate G-code directly inside the software without needing to export files to a separate slicer. Reviewers say this works well for basic prints, but also note that it lacks the advanced controls and fine-tuning options found in dedicated 3D printing tools. It’s convenient, but may fall short for users who need more granular print settings.
For example, while you can set infill patterns and layer heights, it doesn’t have as many advanced support generation options. If you’re working on prints that require intricate support structures or highly optimized slicing strategies, you’ll probably still want to use a dedicated slicer.
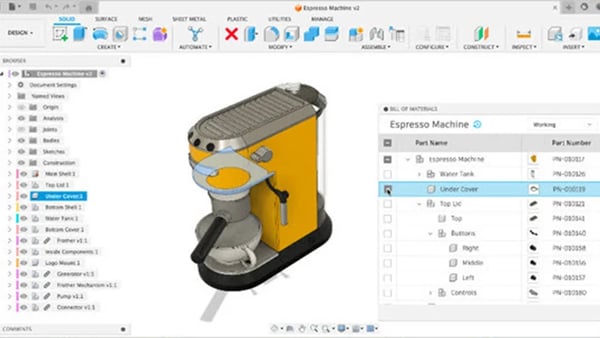
Yanatec reviewers often highlight Autodesk Fusion’s mesh repair tools as a helpful feature for 3D printing workflows. For users dealing with non-manifold geometry, holes, or broken STLs, the built-in repair tool has been noted for catching common issues and offering automatic fixes—reducing the need for third-party tools like Netfabb. While some complex files still require manual cleanup, many users say Fusion’s repair process is efficient enough to get files print-ready in tools like Cura without much extra effort.
Another standout is the ability to switch between parametric and freeform modeling. Reviews frequently mention how this flexibility supports both precise engineering parts and more organic, sculpted shapes. Being able to jump between structured modeling and intuitive sculpting gives users more creative control compared to platforms that lock them into a single workflow.
That said, the UI is often described as dense—powerful, but potentially overwhelming for users focused solely on preparing a model for 3D printing. Several reviewers point out that even simple edits can involve multiple menu layers, which can slow things down for casual users or quick jobs.
Performance with high-poly STL files is another area where Fusion shows limitations. According to feedback, importing large, detailed models can cause noticeable slowdowns, even on high-spec machines. The platform seems better optimized for native Fusion files, so users working regularly with scanned or sculpted assets may need to adjust expectations around speed and responsiveness.
Key Features:
✔ Parametric & direct modeling
✔ Cloud collaboration & version control
✔ Built-in CAM and simulation tools
✔ STL export for 3D printing
Pros:
✅ Free for personal use (with limitations)
✅ Strong community & tutorials
✅ Supports both simple and complex designs
Cons:
❌ Steeper learning curve than TinkerCAD
❌ Requires a decent PC for smooth performance
Pricing: Free for personal use, $70/month for professionals
3. FreeCAD
Best for: Open-source enthusiasts, engineers, and budget-conscious users.
Description:
FreeCAD is a free, open-source parametric 3D modeling tool designed for mechanical engineering and product design. It’s highly customizable and supports Python scripting.
Key Features:
✔ Parametric modeling
✔ Modular architecture (add-ons available)
✔ Supports STEP, STL, OBJ exports
✔ Active open-source community
Pros:
✅ Completely free
✅ Great for technical & functional parts
✅ No restrictions on commercial use
Cons:
❌ Outdated UI compared to paid software
❌ Not ideal for organic shapes
Pricing: Free
4. SketchUp
🔗 Official Website
Best for: Architects, woodworkers, and 3D printing beginners.
Description:
SketchUp is known for its intuitive, user-friendly interface, making it great for architectural and artistic models. The free version (SketchUp Free) is web-based, while SketchUp Pro offers advanced features.
Key Features:
✔ Easy push-pull modeling
✔ Large 3D model library (Warehouse)
✔ STL export via plugins
Pros:
✅ Simple learning curve
✅ Great for architectural designs
✅ Free version available
Cons:
❌ Limited precision for engineering
❌ STL export requires extension (paid in Pro)
Pricing: Free (web), $299/year (Pro)
5. Onshape
🔗 Official Website
Best for: Collaborative teams and cloud-based CAD users.
Description:
Onshape is a fully cloud-based CAD software with real-time collaboration features, making it ideal for teams and remote work. It supports parametric and direct modeling.
Key Features:
✔ Browser-based (no installation)
✔ Real-time collaboration
✔ Version history & cloud storage
✔ STL export for 3D printing
Pros:
✅ No software installation needed
✅ Excellent for teamwork
✅ Free plan available
Cons:
❌ Requires internet connection
❌ Free plan has limited private documents
Pricing: Free (public docs), $1,500/year (Professional)
6. Blender
Best for: Artists, animators, and organic 3D modeling.
Features:
✔ Advanced mesh modeling & sculpting
✔ Open-source and completely free
✔ Supports STL, OBJ, and 3MF exports
✔ Powerful rendering and animation tools
Pros:
- Free with no restrictions
- Great for figurines, characters, and artistic designs
- Large community with tutorials
Cons:
- Steep learning curve for beginners
- Not optimized for mechanical/engineering designs
Pricing: Free
7. SolidWorks
Best for: Engineers, product designers, and professionals.
Features:
✔ Parametric and surface modeling
✔ Simulation and stress analysis tools
✔ Direct STL export for 3D printing
✔ Large parts library
Pros:
- Industry-standard for mechanical design
- High precision and professional-grade tools
- Good support and training resources
Cons:
- Expensive (no free version)
- Requires powerful hardware
Pricing: Starts at $3,995/year
8. OpenSCAD
Best for: Programmers and technical designers.
Features:
✔ Code-based modeling (no GUI drag-and-drop)
✔ Precise control over dimensions
✔ Lightweight and open-source
Pros:
- Free and script-driven (ideal for automation)
- Great for mathematical/parametric designs
- No complex UI to learn
Cons:
- Not user-friendly for non-coders
- Limited for artistic models
Pricing: Free
9. Rhino 3D (Rhinoceros)
Best for: Architects, industrial designers, and advanced users.
Features:
✔ NURBS-based modeling (high precision)
✔ Supports plugins like Grasshopper for parametric design
✔ STL, OBJ, and STEP export
Pros:
- Excellent for complex curves and surfaces
- One-time purchase (no subscription)
- Widely used in professional industries
Cons:
- Expensive for hobbyists
- Steeper learning curve than TinkerCAD/Fusion 360
Pricing: $995 (one-time payment)
10. ZBrush
Best for: Digital sculptors, game artists, and organic modeling.
Features:
✔ High-detail sculpting tools
✔ Dynamic mesh refinement
✔ 3D printing export (STL, OBJ)
Pros:
- Industry-leading for character/creature design
- Real-time clay-like sculpting
- Great for figurines and jewelry
Cons:
- Expensive
- Overkill for mechanical parts
Pricing: $895 (one-time payment)
How to Choose the Right CAD Software for Your Needs
- For absolute beginners: Start with TinkerCAD or SketchUp.
- For mechanical designs: Try Fusion 360 or FreeCAD.
- For artistic models: Blender or ZBrush are best.
- For professionals: SolidWorks or Rhino 3D offer advanced tools.
Free vs. Paid CAD Software: Which is Better?
| Feature | Free CAD Software | Paid CAD Software |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | $0 | $50–$5000/year |
| Features | Limited | Advanced |
| Support | Community-based | Professional support |
| Best for | Beginners, hobbyists | Professionals, businesses |
Common Mistakes Beginners Make with 3D Printing CAD
❌ Ignoring file formats – Always export as STL or OBJ.
❌ Overcomplicating designs – Start simple.
❌ Skipping tutorials – Learning shortcuts saves time.
❌ Ignoring wall thickness – Too thin = fragile prints.
FAQs About 3D Printing CAD Software
Q1. What is the easiest CAD software for 3D printing?
A: TinkerCAD is the easiest for beginners.
Q2. Is Fusion 360 free?
A: Yes, for personal use (with some limitations).
Q3. Can I use Blender for 3D printing?
A: Yes, but it’s better for artistic models than engineering.
Experiment with free versions before committing to paid software. Happy designing! 🚀
🔗 Further Reading:

yanatec.in Best ai for image generation of 2025, New car and bike update, ArtCAM 2018 and tech news, software reviews update.